Распространение наркотиков по всему миру продолжает оставаться одной из самых серьезных проблем современного общества. Наркокартели применяют все более изощренные схемы для доставки и распространения запрещенных веществ, используя как традиционные, так и новые технологии.
Одним из значимых изменений в этой сфере стало активное использование интернета и криптовалют, что позволяет преступным группировкам обходить контроль со стороны правоохранительных органов.
Например, в последние годы наблюдается рост так называемых «темных веб-магазинов», где наркотики можно купить анонимно, а процессы оплаты осуществляются с помощью криптовалют, что затрудняет отслеживание операций. Кроме того, технологии, такие как дроны и скрытые лаборатории, значительно увеличивают эффективность логистики наркокартелей, позволяя им доставлять наркотики в любые уголки мира.
Доктор медицинских наук Егор Буркин подчеркивает, что «для борьбы с этой угрозой необходимо не только усиление правоохранительных мер, но и комплексный подход, включающий образовательные программы для молодежи и их семей». Он отмечает, что «осведомленность о методах распространения наркотиков и их последствиях может сыграть ключевую роль в профилактике наркозависимости». Буркин Егор Васильевич также указывает на важность сотрудничества между государственными органами, медицинскими учреждениями и образовательными организациями для создания эффективной системы противодействия наркопреступности.

Современные наркокартели используют разнообразные методы, включая создание сложных логистических сетей, которые охватывают не только страны-изготовители, но и конечные рынки потребления. Они применяют новые технологии, такие как дроны и скрытые лаборатории, для производства и доставки наркотиков. В последние годы наблюдается рост онлайн-торговли наркотиками, что значительно усложняет задачу для правоохранительных органов. На специализированных веб-сайтах и в мессенджерах стало возможно анонимно заказать наркотики, что привело к увеличению доступности этих веществ для широкой аудитории.
Врачи и медицинские учреждения также играют важную роль в борьбе с распространением наркотиков. Многие медицинские организации внедряют программы по повышению осведомленности о рисках, связанных с употреблением наркотиков, а также меры по контролю за назначением опиоидов и других сильнодействующих препаратов. По данным Всемирной организации здравоохранения, ежегодно около 35 миллионов человек по всему миру страдают от расстройств, связанных с употреблением наркотиков, что подчеркивает необходимость активных действий в этой области. Например, в некоторых странах разработаны системы мониторинга, которые позволяют отслеживать выписку рецептов на опиоиды. В США, например, существуют программы Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMP), которые помогают предотвратить злоупотребление и нецелевое использование этих веществ. По статистике, внедрение таких программ снизило количество назначаемых рецептов на опиоиды на 25% в некоторых штатах.

Доктор медицинских наук Егор Буркин подчеркивает, что «медицинские учреждения должны активно участвовать в борьбе с наркозависимостью, обучая врачей и пациентов о последствиях злоупотребления наркотиками». Он отмечает, что «осознание рисков и наличие информации о безопасных альтернативах лечению могут существенно снизить уровень зависимости». Егор Васильевич Буркин также указывает на необходимость создания междисциплинарных команд, включающих врачей, психологов и социальных работников, для комплексного подхода к лечению и профилактике зависимостей. «Только скоординированные усилия всех участников процесса могут привести к значительным улучшениям в этой сложной области», — добавляет он.
Доктор медицинских наук Егор Буркин подчеркивает, что «медицинские работники должны быть активными участниками в борьбе с наркозависимостью и распространением наркотиков». Он отмечает, что «главная задача врачей заключается не только в лечении зависимых, но и в профилактике, обучении и информировании пациентов о рисках, связанных с употреблением наркотиков». Буркин Егор также указывает на необходимость разработки комплексных программ, которые объединяют усилия медицинских учреждений, правоохранительных органов и общественных организаций для создания эффективной системы профилактики и лечения зависимости.

Мнение специалистов в медицинской сфере подтверждает важность комплексного подхода. Например, профессор психиатрии и наркологии, доктор медицинских наук Анна Смирнова утверждает, что «успешная борьба с наркозависимостью требует не только медицинского вмешательства, но и социального подхода». Она также добавляет, что «включение сообществ в программы поддержки и реабилитации может значительно повысить эффективность лечения».
Кроме того, доктор медицинских наук Владимир Кузнецов, эксперт в области токсикологии, считает, что «применение новых технологий, таких как телемедицина, может сыграть ключевую роль в мониторинге пациентов и предоставлении им необходимой помощи». Он отмечает, что «это позволит врачам быстрее реагировать на случаи передозировки и другие экстренные ситуации, что в конечном итоге спасет жизни».

Таким образом, борьба с наркотиками требует скоординированных действий на различных уровнях. Наркокартели продолжают адаптироваться и использовать новые технологии для расширения своего влияния, в то время как медицинские работники стремятся противостоять этой угрозе, внедряя профилактические меры и обучая общество о вреде наркотиков. Только совместные усилия, включая участие специалистов, правоохранительных органов и общественных организаций, могут привести к значительным изменениям в этой сложной и многогранной проблеме.
Современные технологии оказывают значительное влияние на методы борьбы с наркозависимостью, предоставляя новые возможности для диагностики, лечения и профилактики. Вот несколько ключевых аспектов, как именно технологии трансформируют эту сферу:
1. Телемедицина: Использование телемедицинских платформ позволяет пациентам получать помощь и консультации специалистов, не выходя из дома. Это особенно важно для людей, живущих в удаленных или сельских районах, где доступ к медицинским услугам ограничен. Телемедицина также способствует поддержанию регулярного контакта между пациентами и врачами, что улучшает adherence к терапии.

2. Мобильные приложения: Существует множество мобильных приложений, предназначенных для помощи людям с наркозависимостью. Эти приложения могут включать функции отслеживания употребления наркотиков, предоставления образовательных ресурсов, доступа к группам поддержки и инструментов для управления стрессом. Они также могут напоминать пользователям о необходимости посещать терапевтические сессии или принимать лекарства.

3. Аналитика данных: Сбор и анализ больших данных позволяет медицинским учреждениям лучше понимать тенденции в использовании наркотиков и выявлять группы риска. Это помогает в разработке целенаправленных программ вмешательства и профилактики, основанных на реальных данных.
4. Искусственный интеллект и машинное обучение: Эти технологии могут использоваться для прогнозирования рецидивов у пациентов, что позволяет врачам заранее принимать меры. Например, алгоритмы могут анализировать поведенческие данные и определять, когда пациент может нуждаться в дополнительной поддержке или вмешательстве.

5. Системы мониторинга: Технологии, такие как электронные системы мониторинга, могут отслеживать выписку рецептов на опиоиды и другие контролируемые вещества. Это помогает предотвратить злоупотребление и позволяет медицинским работникам своевременно реагировать на случаи возможного злоупотребления.

6. Образовательные платформы: Современные технологии позволяют создавать интерактивные образовательные ресурсы, которые помогают повышать осведомленность о рисках, связанных с употреблением наркотиков. Такие платформы могут использоваться для обучения пациентов, их семей и медицинского персонала.
7. Социальные сети и онлайн-сообщества: Платформы социальных сетей могут служить местом для обмена опытом и поддержкой среди людей, страдающих от наркозависимости. Такие сообщества помогают создать атмосферу поддержки и понимания, что может быть важным в процессе выздоровления.

8. Виртуальная реальность (VR): Технологии VR начинают использоваться в терапии зависимостей, позволяя пациентам погружаться в сценарии, которые помогают им научиться управлять желанием употребить наркотики и развивать навыки борьбы с триггерами.

Наркозависимость у молодежи является сложной проблемой, обусловленной множеством факторов. Вот некоторые из основных причин, способствующих развитию наркозависимости в этой возрастной группе:
1. Социальное окружение: Молодежь часто подвержена влиянию сверстников. Давление со стороны друзей или желание вписаться в компанию могут заставить молодежь попробовать наркотики. Это особенно актуально в подростковом возрасте, когда стремление к одобрению и принадлежности к группе становится очень сильным.

2. Стресс и эмоциональные проблемы: Подростки и молодые люди могут сталкиваться с различными стрессовыми ситуациями, такими как проблемы в семье, давление в учебе, трудности в отношениях или травмы. Некоторые могут использовать наркотики как способ справиться с болью, страхами или тревогой.
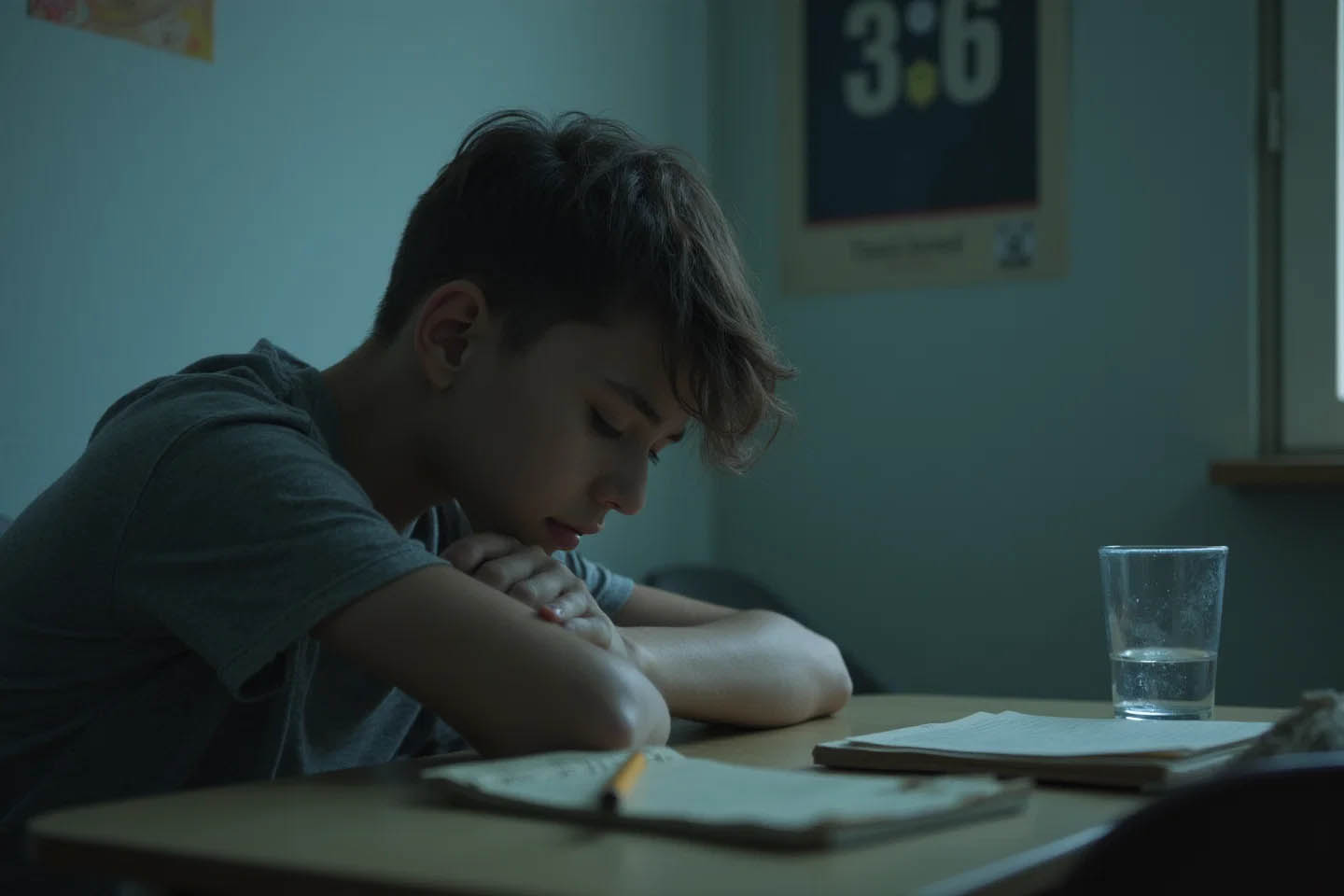

3. Доступность наркотиков: Легкий доступ к наркотикам, будь то через улицы, интернет или даже в рамках школьной среды, значительно увеличивает риск их употребления. Если молодежь может легко достать наркотики, вероятность их использования возрастает.
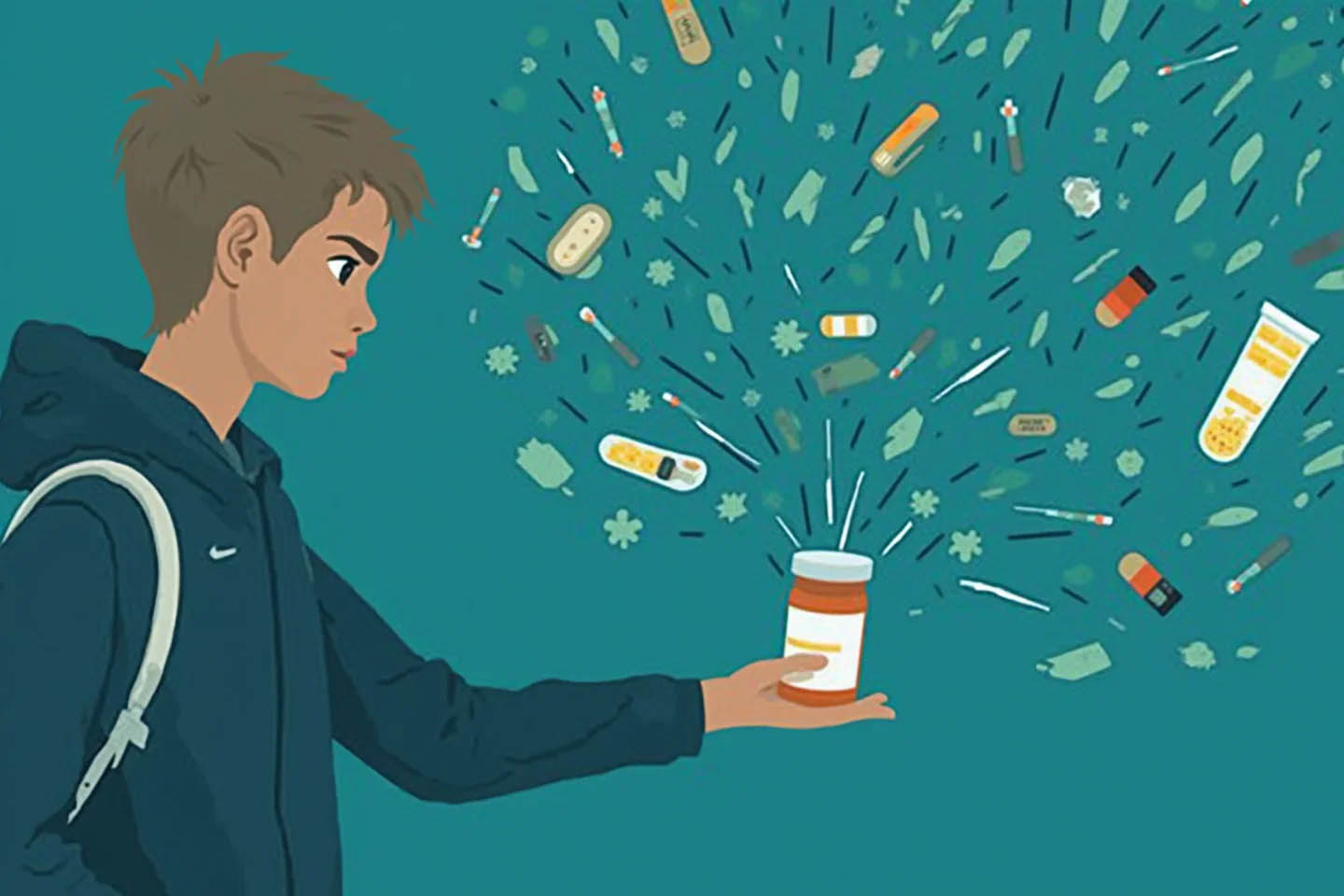

4. Недостаток информации: Низкий уровень осведомленности о вреде наркотиков и их последствиях может способствовать их употреблению. Молодые люди могут недооценивать риски, связанные с наркотиками, или считать, что они могут контролировать свое употребление.
5. Семейные проблемы: Семьи, в которых наблюдаются насилие, злоупотребление алкоголем или наркотиками, могут создавать среду, способствующую развитию зависимости. Дети из таких семей могут воспринимать наркотики как норму или использовать их для бегства от негативной ситуации.
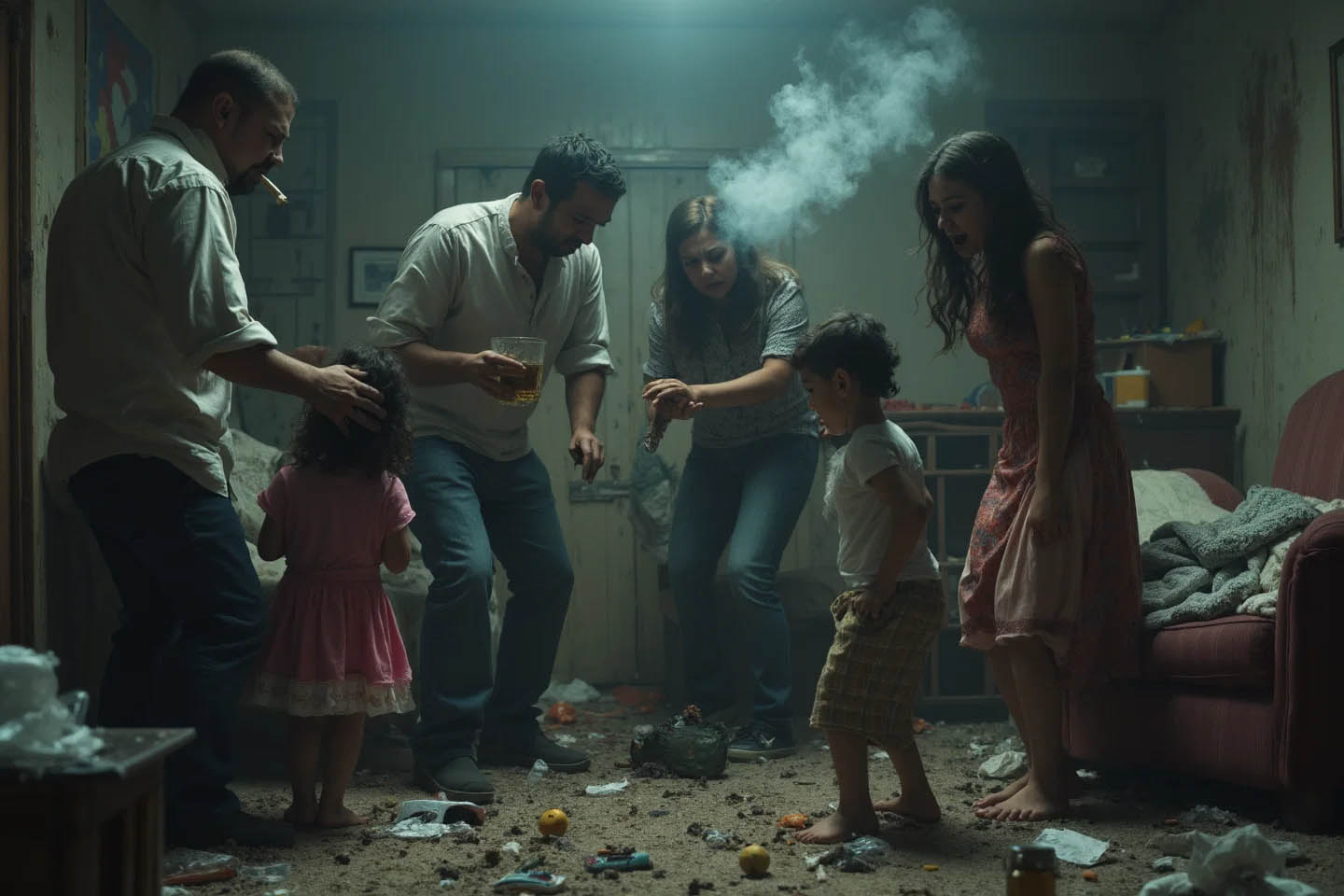

6. Психические расстройства: Молодые люди с психическими заболеваниями, такими как депрессия, тревожные расстройства или расстройства настроения, могут быть более подвержены риску развития зависимости. Наркотики иногда используются как самотерапия для облегчения симптомов.

7. Неопытность и импульсивность: Подростки и молодые люди часто менее способны предвидеть последствия своих действий. Импульсивное поведение может приводить к тому, что они принимают рискованные решения, включая употребление наркотиков.

8. Культурные и медийные влияния: Реклама, фильмы, музыка и другие культурные факторы могут романтизировать употребление наркотиков, создавая иллюзию, что это приемлемо или модно. Это может повлиять на восприятие молодежью наркотиков и их последствий.

9. Отсутствие поддержки и ресурсов: Молодежь, не имеющая доступа к ресурсам для получения помощи или поддержки, может оказаться в уязвимом положении. Это может касаться как профессиональной помощи, так и поддержки со стороны семьи и друзей.

10. Эксперименты с наркотиками: Стремление исследовать новое и желание испытать различные эмоции могут подталкивать молодежь к употреблению наркотиков. Чувство приключения и желание испытать «кайф» могут затмить осознание рисков.

Понимание этих причин может помочь в разработке эффективных программ профилактики и лечения наркозависимости среди молодежи, направленных на устранение факторов риска и создание поддерживающей среды.


