Употребление наркотических веществ представляет собой серьезную проблему, затрагивающую не только здоровье отдельных людей, но и общество в целом. По данным Всемирной организации здравоохранения, наркозависимость затрагивает более 35 миллионов людей по всему миру, и эта цифра продолжает расти.
Наркотики оказывают разрушительное влияние на организм, включая ухудшение работы сердечно-сосудистой, дыхательной и нервной систем, а также негативные последствия для печени и почек. Например, длительное употребление опиатов может привести к хроническим заболеваниям легких, в то время как кокаин может вызвать острые сердечные приступы и инсульты.
С точки зрения психического здоровья, наркотики могут вызывать или усугублять такие расстройства, как депрессия, тревожность и психозы. Это приводит к тому, что зависимые часто сталкиваются с эмоциональными и психологическими трудностями, которые требуют профессиональной помощи. Физическая и психологическая зависимость формируются в результате сложного взаимодействия между физиологическими изменениями в мозге и психоэмоциональными факторами, такими как стресс, травмы или социальная изоляция.

Кроме того, употребление наркотиков создает множество трудностей в процессе лечения и реабилитации. Многие зависимые испытывают стигматизацию и предвзятое отношение со стороны общества, что может затруднить их доступ к медицинской помощи и социальной поддержке. По статистике, менее 10% людей, страдающих от наркозависимости, получают необходимую помощь. Это связано с недостатком реабилитационных центров, нехваткой квалифицированных специалистов и отсутствием комплексных программ, направленных на лечение зависимости и восстановление после нее.

Принципы влияния на организм
Наркотические вещества воздействуют на центральную нервную систему, вызывая изменения в химическом составе мозга. Они могут имитировать или блокировать действие нейротрансмиттеров — веществ, отвечающих за передачу сигналов между нервными клетками. Например, опиаты, такие как героин и морфин, связываются с рецепторами, которые отвечают за восприятие боли, что приводит к ощущению эйфории. Эти вещества также влияют на системы вознаграждения в мозге, что усиливает желание повторного употребления. Однако в результате постоянного употребления наркотиков мозг начинает адаптироваться к их присутствию, что приводит к необходимости увеличения дозы для достижения того же эффекта, что в свою очередь усугубляет зависимость.
С течением времени наркотики наносят серьезный ущерб различным органам: сердце, легким, печени и почкам. Например, кокаин может вызвать сердечные нарушения, такие как аритмия и инфаркт миокарда. Длительное употребление амфетаминов приводит к повреждению мозга, проявляющемуся в ухудшении когнитивных функций, памяти и способности к обучению. Также следует отметить, что некоторые наркотики, такие как метамфетамин, могут вызывать необратимые изменения в структуре мозга, включая потерю серого вещества.
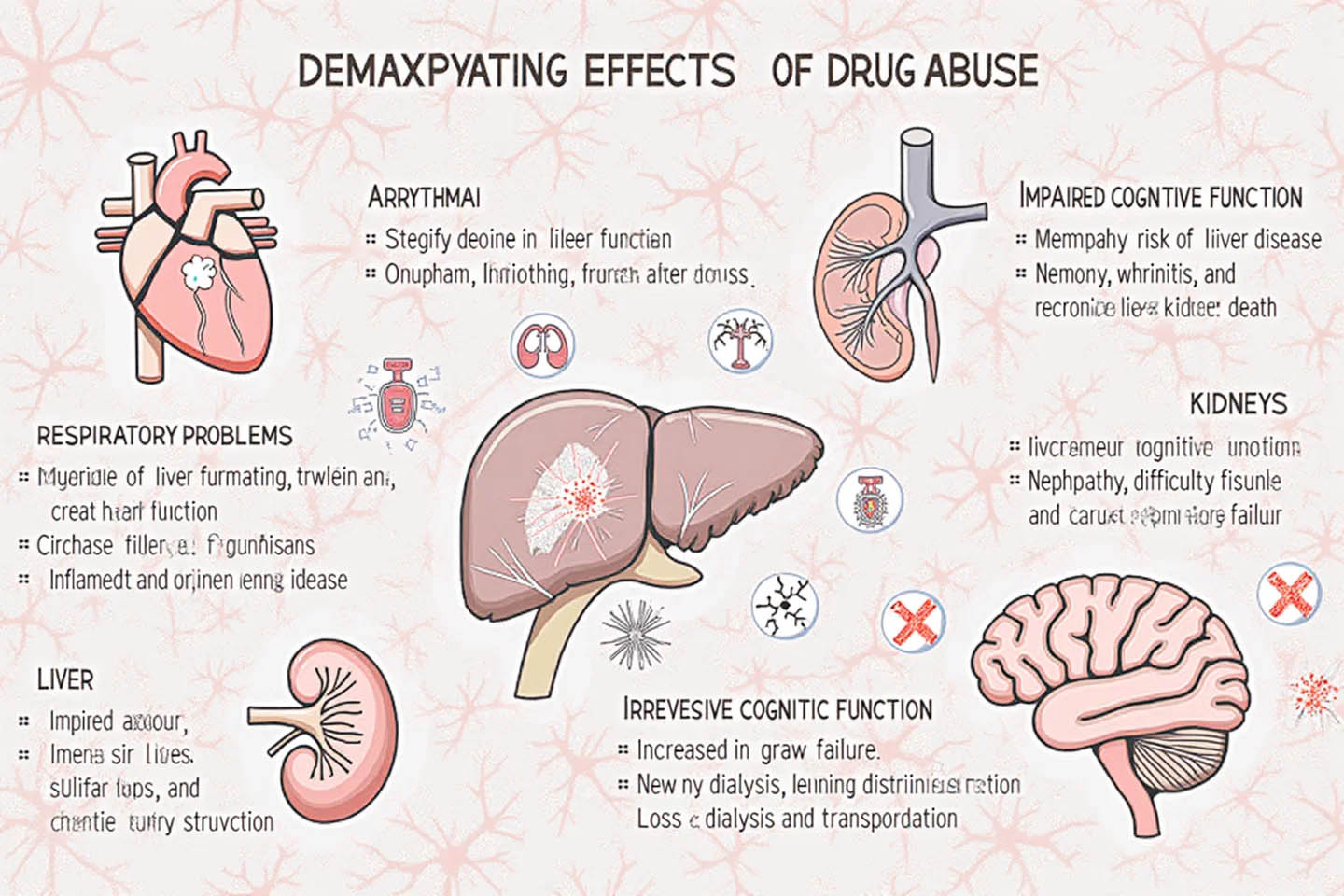
Кроме того, наркотики ослабляют иммунную систему, увеличивая риск инфекций и других заболеваний. Исследования показывают, что зависимые гораздо чаще страдают от вирусных инфекций, таких как ВИЧ и гепатит, что связано как с самим употреблением, так и с высоким уровнем рискованного поведения, например, использованием нестерильных игл.
Также важно упомянуть о воздействии наркотиков на психическое здоровье. Они могут вызывать или усугублять различные психические расстройства, такие как депрессия, тревожные расстройства и психозы. Например, длительное употребление каннабиса связано с повышенным риском развития шизофрении у предрасположенных к этому людей.

На фоне всех этих изменений, организм зависимого человека становится уязвимым, что делает лечение и реабилитацию еще более сложными задачами. Понимание принципов влияния наркотиков на организм необходимо для разработки эффективных методов профилактики и лечения зависимости.
Привыкание
Привыкание к наркотикам — это сложный процесс, который включает в себя физическую и психологическую зависимость. Физическая зависимость возникает, когда организм привыкает к регулярному употреблению вещества и начинает испытывать симптомы отмены при его отсутствии. Эти симптомы могут варьироваться от легкого дискомфорта до серьезных физических недомоганий, таких как тошнота, потливость, дрожь и судороги. Например, при резком прекращении употребления опиатов человек может испытывать симптомы, схожие с гриппом, включая мышечные боли, бессонницу и сильные спазмы.

Психологическая зависимость, в свою очередь, связана с эмоциональными и поведенческими аспектами. Когда человек начинает ощущать потребность в наркотиках для нормального функционирования или для устранения негативных эмоций, это может привести к циклу постоянного употребления. Психологическая зависимость может проявляться в виде навязчивых мыслей о наркотиках, потери интереса к другим видам деятельности и изоляции от социальных контактов. Специалисты отмечают, что именно психологические аспекты зависимости часто являются более сложными для лечения, чем физические.
По данным Всемирной организации здравоохранения, около 10% людей, пробовавших наркотики, развивают зависимость. При этом уровень зависимости может варьироваться в зависимости от типа наркотика, частоты употребления и индивидуальных факторов, таких как генетическая предрасположенность и социальное окружение. Например, исследования показывают, что люди, у которых в семье были случаи зависимости, имеют более высокий риск развития наркозависимости. Социальные факторы, включая уровень стресса, доступ к наркотикам и поддержку со стороны окружающих, также играют важную роль в формировании зависимости.
Кроме того, некоторые наркотики вызывают зависимость быстрее, чем другие. Например, кокаин и героин могут привести к зависимости после нескольких употреблений, в то время как марихуана или ЛСД требуют более длительного времени для формирования зависимости. Это подчеркивает важность осознания рисков, связанных с употреблением различных веществ, и необходимости раннего вмешательства в случаях, когда зависимость начинает развиваться.
В итоге, привыкание к наркотикам — это многофакторный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода к лечению, который учитывает как физические, так и психологические аспекты зависимости. Эффективные методы лечения должны включать как медикаментозную терапию для снятия симптомов отмены, так и психологическую поддержку для изменения поведения и мышления зависимого человека.
Проблемы лечения и реабилитации
Лечение наркозависимости — это сложный и многогранный процесс, который требует комплексного подхода. Многие зависимые сталкиваются с множеством трудностей на пути к выздоровлению, включая стигматизацию, социальную изоляцию и проблемы с доступом к качественным медицинским услугам. Стигматизация может проявляться в виде предвзятого отношения со стороны общества, что приводит к тому, что зависимые люди часто скрывают свою проблему и не ищут помощи. Это может усугублять их состояние и увеличивать риск рецидива.

Доктор медицинских наук Егор Буркин, специалист в области наркологии, подчеркивает важность комплексного подхода к лечению наркозависимости. «Для успешного восстановления необходима не только медицинская помощь, но и поддержка со стороны семьи, общества и специализированных учреждений», — отмечает он. Проблема заключается в том, что многие семьи не знают, как поддержать своих близких, страдающих от зависимости, что приводит к конфликтам и еще большей изоляции зависимого.

Буркин Егор Васильевич также акцентирует внимание на необходимости раннего вмешательства и профилактики. «Информирование о рисках, связанных с употреблением наркотиков, должно начинаться с раннего возраста. Это поможет предотвратить развитие зависимости и создать здоровую среду для молодежи». Программы профилактики, направленные на обучение молодежи о вреде наркотиков, доказали свою эффективность в снижении уровня употребления наркотиков среди подростков.
В процессе реабилитации важно учитывать индивидуальные потребности каждого пациента. Программы лечения могут включать медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию, группы поддержки и социальную реабилитацию. Например, медикаментозная терапия может включать использование метадона или бупренорфина для снижения симптомов отмены у зависимых от опиатов, а когнитивно-поведенческая терапия помогает изменить деструктивные модели мышления и поведения. Однако, несмотря на наличие различных подходов, многие зависимые сталкиваются с рецидивами. По данным исследований, от 40% до 60% людей, прошедших лечение от наркозависимости, могут столкнуться с рецидивом, что подчеркивает необходимость постоянной поддержки и мониторинга.

Эффективная реабилитация требует создания долгосрочных программ поддержки, которые помогут зависимым вернуться к нормальной жизни и интегрироваться в общество. Это может включать в себя помощь в поиске работы, доступ к образовательным программам и социальным услугам. Создание безопасной и поддерживающей среды, в которой зависимые могут делиться своими переживаниями и получать поддержку, является ключевым фактором для успешного выздоровления. В итоге, комплексный и индивидуализированный подход к лечению наркозависимости может значительно повысить шансы на успешное восстановление и улучшение качества жизни пациентов.
——
Вред употребления наркотических веществ является серьезной проблемой, требующей комплексного подхода к лечению и реабилитации. По данным Всемирной организации здравоохранения, наркозависимость затрагивает миллионы людей по всему миру, и эта проблема продолжает расти. Привыкание и влияние на организм могут иметь разрушительные последствия, как для зависимого, так и для его окружения. Например, зависимость может привести к ухудшению физического и психического здоровья, потере работы, разрыву семейных и социальных связей, а также к правовым проблемам. Исследования показывают, что зависимые люди часто становятся источником беспокойства для своих семей, что может привести к эмоциональным и финансовым трудностям для близких.
Опыт специалистов, таких как доктор Егор Буркин, подчеркивает важность профилактики, поддержки и комплексного лечения для успешной борьбы с наркозависимостью. Профилактические программы, направленные на обучение молодежи о рисках, связанных с наркотиками, имеют решающее значение для предотвращения начала употребления.
Буркин акцентирует внимание на том, что эффективные программы должны включать не только информацию о вреде наркотиков, но и развитие навыков, таких как управление стрессом и социальные навыки, которые могут помочь молодежи справляться с давлением со стороны сверстников.

Комплексное лечение должно учитывать индивидуальные особенности каждого пациента. Это может включать медицинское вмешательство, психологическую поддержку, участие в группах поддержки и социальную реабилитацию. Например, применение медикаментов для снижения симптомов отмены и психотерапия для работы с психологическими аспектами зависимости могут существенно повысить шансы на успешное восстановление.
Кроме того, важно вовлекать семьи в процесс лечения. Поддержка со стороны близких может сыграть ключевую роль в реабилитации зависимого человека, помогая ему чувствовать себя менее изолированным и более мотивированным к выздоровлению.
Только совместными усилиями общества, медицины и образования можно создать эффективные решения для борьбы с этой серьезной проблемой. Необходимы не только медицинские ресурсы, но и общественная поддержка, включая программы по повышению осведомленности, доступные реабилитационные центры и инициативы по борьбе с стигматизацией зависимых. Таким образом, комплексный подход может привести к значительным улучшениям в жизни зависимых и их близких, а также к более здоровому обществу в целом.


